在之前的基础上改进了一部分
硬件上把串口和SWD下载口引出来了,夹具下载有点不稳定
同时把手头上的LCD模组和红外传感器模组给用了,没有额外购买物资,成品图如下:

左边是V1,右边是V2
软件部分增加了一些图像处理的功能:
图像平滑:
双线性插值
void interpolateTemperature(float *src, float *dst, uint8_t src_w, uint8_t src_h, uint8_t dst_w, uint8_t dst_h) {
float x_ratio = (float)(src_w-1) / dst_w;
float y_ratio = (float)(src_h-1) / dst_h;
for (int y = 0; y < dst_h; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < dst_w; x++) {
float x_src = x * x_ratio;
float y_src = y * y_ratio;
int x0 = (int)x_src, y0 = (int)y_src;
float x_diff = x_src - x0;
float y_diff = y_src - y0;
float val = src[y0*src_w + x0] * (1-x_diff)*(1-y_diff)
+ src[y0*src_w + x0+1] * x_diff*(1-y_diff)
+ src[(y0+1)*src_w + x0] * (1-x_diff)*y_diff
+ src[(y0+1)*src_w + x0+1] * x_diff*y_diff;
dst[y*dst_w + x] = val;
}
}
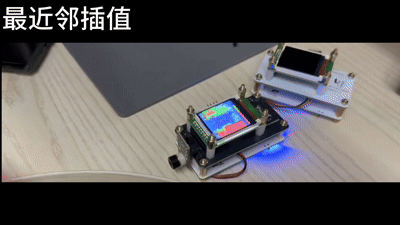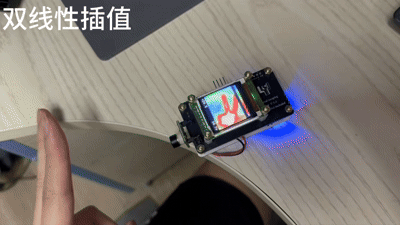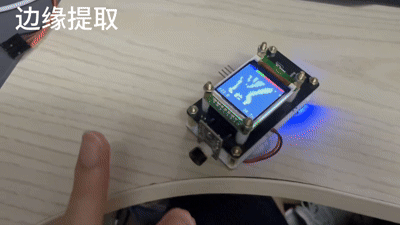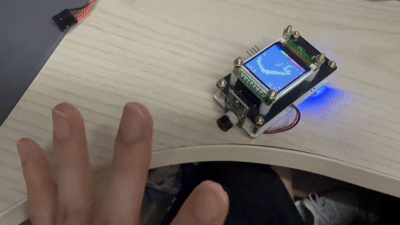
}最近邻插值
void nearestNeighborInterpolate(float *src, float *dst, uint8_t src_w, uint8_t src_h, uint8_t dst_w, uint8_t dst_h) {
float x_ratio = (float)src_w / dst_w;
float y_ratio = (float)src_h / dst_h;
for (int y = 0; y < dst_h; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < dst_w; x++) {
int src_x = (int)(x * x_ratio);
int src_y = (int)(y * y_ratio);
// 防止越界
if (src_x >= src_w) src_x = src_w - 1;
if (src_y >= src_h) src_y = src_h - 1;
dst[y * dst_w + x] = src[src_y * src_w + src_x];
}
}
}边缘提取
// Sobel 算子卷积核
const int sobel_x[3][3] = {
{-1, 0, 1},
{-2, 0, 2},
{-1, 0, 1}
};
const int sobel_y[3][3] = {
{-1, -2, -1},
{ 0, 0, 0},
{ 1, 2, 1}
};
void detectEdges(float *input, uint8_t *output, uint8_t width, uint8_t height) {
for (int y = 1; y < height - 1; y++) {
for (int x = 1; x < width - 1; x++) {
float gx = 0, gy = 0;
// 3x3 邻域卷积
for (int j = -1; j <= 1; j++) {
for (int i = -1; i <= 1; i++) {
float pixel = input[(y + j) * width + (x + i)];
gx += pixel * sobel_x[j + 1][i + 1];
gy += pixel * sobel_y[j + 1][i + 1];
}
}
uint8_t edge_strength = (uint8_t)(fabs(gx) + fabs(gy));
edge_strength = (edge_strength > 255) ? 255 : edge_strength;
output[y * width + x] = edge_strength;
}
}
}
static void drawPicture3(void) {
uint8_t cell_size = 4;
uint8_t start_x = 0;
uint8_t start_y = 16;
float interpolated_temp[32 * 24];
uint8_t edge_map[32 * 24];
//双线性插值
interpolateTemperature(tempValues, interpolated_temp, 32, 24, 32, 24);
//边缘检测
detectEdges(interpolated_temp, edge_map, 32, 24);
//只绘制边缘(白色),其余区域黑色
for (int y = 0; y < 24; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < 32; x++) {
uint16_t color = ST7735_BLACK; // 默认黑色
// 如果边缘强度足够高,则显示白色
if ((edge_map[y * 32 + x] > 10 ) && (edge_map[y * 32 + x] < 40 )){ // 阈值可调
color = ST7735_WHITE;
}
ST7735_FillRectangle(
start_x + x * cell_size,
start_y + (23 - y) * cell_size,
cell_size,
cell_size,
color
);
}
}
}
图像识别
准备往设备里嵌一个轻量级的神经网络,尝试一下更深层次的边缘计算
应用场景是经典手势识别,设置了1~5的数据集,其实就是自己用串口传到PC进行数据清洗
网络结构如下:
- 特征提取层:包含两个步长为2的3x3卷积层(通道数从1→4→8),每层后接ReLU激活,将输入从 [1,32,24] 逐步下采样至 [8,8,6]。
- 分类器层:将特征展平后,经过一个8维的线性层(含ReLU),最终输出5类概率。总参数量约3KB,RAM占用<8KB
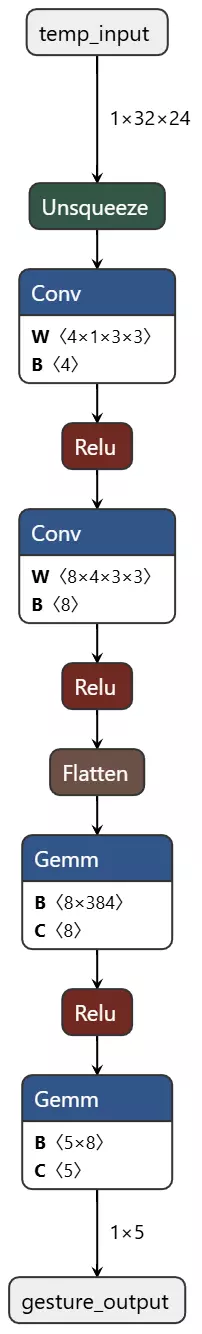
在pyTorch中秒搭建模型
class MicroTempNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=5):
super().__init__()
# 特征提取
self.features = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 4, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1), # [4, 16, 12]
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(4, 8, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1), # [8, 8, 6]
nn.ReLU(),
)
# 分类器 (参数量: 8*8*6*8 + 8 + 8*5 + 5 = 2,669)
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(8*8*6, 8),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(8, num_classes)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = x.unsqueeze(1) # 添加通道维度 [B,1,32,24]
x = self.features(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x将模型以权重模式保存并导出到c头文件
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'micro_temp_net_params.pth')之后将每个部分转C,这里大量使用ai工具,还是比较给力的
// ReLU
static void relu(float* data, int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
data[i] = data[i] > 0 ? data[i] : 0;
}
}
// 2d convolution stride = 2
static void conv2d_stride2(const float* input, const float* weights, const float* bias,
float* output, int in_channels, int out_channels,
int height, int width, int kernel_size) {
int out_h = height / 2;
int out_w = width / 2;
for (int oc = 0; oc < out_channels; oc++) {
for (int oh = 0; oh < out_h; oh++) {
for (int ow = 0; ow < out_w; ow++) {
float sum = bias[oc];
int ih = oh * 2;
int iw = ow * 2;
for (int ic = 0; ic < in_channels; ic++) {
for (int kh = 0; kh < kernel_size; kh++) {
for (int kw = 0; kw < kernel_size; kw++) {
int input_idx = ic * height * width + (ih + kh) * width + (iw + kw);
int weight_idx = oc * in_channels * kernel_size * kernel_size +
ic * kernel_size * kernel_size +
kh * kernel_size + kw;
sum += input[input_idx] * weights[weight_idx];
}
}
}
int output_idx = oc * out_h * out_w + oh * out_w + ow;
output[output_idx] = sum;
}
}
}
}
// fc
static void dense(const float* input, const float* weights, const float* bias,
float* output, int in_features, int out_features) {
for (int i = 0; i < out_features; i++) {
output[i] = bias[i];
for (int j = 0; j < in_features; j++) {
output[i] += input[j] * weights[i * in_features + j];
}
}
}
// initialize
void micro_temp_net_init(MicroTempNet* net,
const float* conv1_w, const float* conv1_b,
const float* conv2_w, const float* conv2_b,
const float* fc1_w, const float* fc1_b,
const float* fc2_w, const float* fc2_b) {
net->conv1_weight = conv1_w;
net->conv1_bias = conv1_b;
net->conv2_weight = conv2_w;
net->conv2_bias = conv2_b;
net->fc1_weight = fc1_w;
net->fc1_bias = fc1_b;
net->fc2_weight = fc2_w;
net->fc2_bias = fc2_b;
}
// predict
void micro_temp_net_predict(const MicroTempNet* net, float* input, float* output) {
// [1,32,24] -> [4,16,12]
float conv1_out[4 * 16 * 12];
conv2d_stride2(input, net->conv1_weight, net->conv1_bias, conv1_out, 1, 4, 32, 24, 3);
relu(conv1_out, 4 * 16 * 12);
// [4,16,12] -> [8,8,6]
float conv2_out[8 * 8 * 6];
conv2d_stride2(conv1_out, net->conv2_weight, net->conv2_bias, conv2_out, 4, 8, 16, 12, 3);
relu(conv2_out, 8 * 8 * 6);
// [8,8,6] -> 384
float flattened[8 * 8 * 6];
memcpy(flattened, conv2_out, sizeof(flattened));
// 384->8
float fc1_out[8];
dense(flattened, net->fc1_weight, net->fc1_bias, fc1_out, 8 * 8 * 6, 8);
relu(fc1_out, 8);
// 8->5
dense(fc1_out, net->fc2_weight, net->fc2_bias, output, 8, NUM_CLASSES);
}主函数里按数据预处理,推理,分类的顺序写了逻辑,注意要和python中一样把数据归一化
void CNN_PROC(void){
//input
for (int y = 0; y < 24; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < 32; x++){
input[y * 32 + x] = tempValues[(31- x) + (y * 32)];
}
}
z_score_normalize(input,768);
// airun
float output[NUM_CLASSES];
micro_temp_net_predict(&CNNmodel, input, output);
// postproc
int predicted_class = 0;
float max_prob = output[0];
for (int i = 1; i < NUM_CLASSES; i++) {
if (output[i] > max_prob) {
max_prob = output[i];
predicted_class = i;
}
}
predicted_class += 1;
sprintf(tempbuffer, "%d " , predicted_class);
ST7735_WriteString(65, 115, tempbuffer, Font_7x10, ST7735_WHITE, ST7735_BLACK);
}
void z_score_normalize(float* input, int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
input[i] = (input[i] - INPUT_MEAN) / INPUT_STD;
}
}不过最后分类效果有点烂,就3和5效果比较好,当作一次边缘设备部署ai的经历还是挺有趣的

